Solar PV Array in Jamaica: A Practical Design Guide with Real 600W Panels
 Dec 01,2025
Dec 01,2025
 sunchees solar system
sunchees solar system
Designing a solar PV array in Jamaica rarely starts with theory. It starts with very practical questions:
-
How many solar panels per string are safe?
-
Will the voltage still be safe on very hot or unusually cold days?
-
How do I combine a solar panel array, inverter, and lithium battery without hidden compatibility issues?
-
On an island with floods and storms, where should I actually put the hardware?

This guide walks through a simple, reusable method for designing a solar photovoltaic array using real numbers from Sunchees components as an example:
-
a 600W shingled module,
-
a 20kW off grid inverter,
-
a 192V lithium battery, and
-
a 120A MPPT charge controller.
It is not a project story. It is a step-by-step design guide you can adapt to your own solar array system, whether you are building a solar array for home, a commercial solar array, or a solar PV array for flood-prone areas in Jamaica or other islands.
Why a Solar PV Array in Jamaica Is a Bit Different
Jamaica and other Caribbean islands have a few things in common:
-
Strong sun (great for any solar power array)
-
Humidity, salt air and storms
-
Local flooding risk in some areas
-
Grid instability in many regions – making off grid solar array and hybrid solar PV array very attractive
That means a solar PV array in Jamaica needs more than just good efficiency:
-
It has to survive storms and transport.
-
It has to stay safe around water and moisture.
-
It has to work well in remote areas where support is limited.
This is where details like PV array string sizing, PV array grounding, and even how you physically place the inverter and battery (wall-mounted vs mobile cabinet) start to matter.
Example System Used in This Guide
To keep the math concrete, we use one representative setup based on Sunchees components. You can replace these with your own hardware later; the method is the same.
Core components (design example)
|
Component type |
Key spec (simplified) |
Notes |
|
600W, Voc 51.45V, Vmp 43.32V, Isc 13.62A, 2279×1134mm |
Shingled 182mm cells, IP68 junction box, optional double glass solar PV array |
|
|
192V, 40.8kWh, max 120A, CAN/RS485 |
Forms a solar battery array for hybrid systems |
|
|
20kW, battery 240V DC, MPPT 130–180V, PV power 9600W |
Core of the off grid inverter PV system |
|
|
120A, MPPT 65–150V, max PV input 5200W |
For a separate 48V solar PV array to battery wiring |
Sunchees can upgrade the 600W modules to double glass, bifacial solar array versions at no extra cost, typically adding around 1.5%+ efficiency and reducing hot-spot risk in high-irradiance island environments.
Step-by-Step: How to Design a Solar PV Array in Jamaica
Below is a compact solar PV array design guide built around the example system. The same logic applies to bigger or smaller systems, ground mounted solar array or rooftop solar array system.
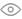
Step 1 – PV array string sizing: how many panels in one string?
For PV array string sizing, you care about:
-
Panel open-circuit voltage (Voc)
-
Temperature coefficient of Voc
-
Maximum DC voltage of your inverter or MPPT
For the 600W panel:
-
Voc = 51.45 V
-
Assume Voc temperature coefficient ≈ –0.30% / °C (typical for 182mm mono)
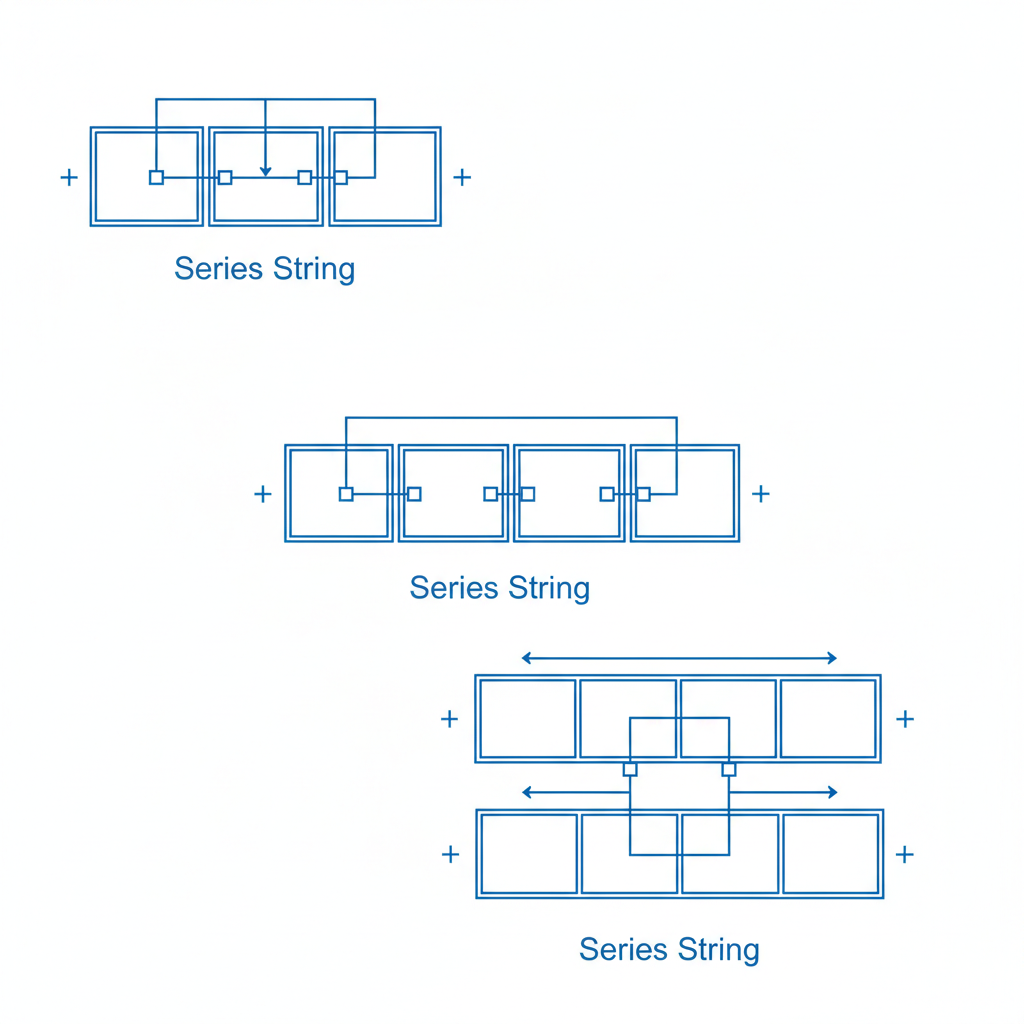
To show the method clearly, we use –10°C as a conservative example for PV array Voc cold temperature. In Jamaica, your real minimum temperature is higher, so the real-world string will be even safer.
Formula
Voc_low = Voc_STC × [1 + (TempCoefVoc × ΔT)]
ΔT = T_min – 25°C
With T_min = –10°C:
-
ΔT = –10 – 25 = –35°C
-
Voltage increase ≈ 0.30% × 35 = 10.5%
-
Voc_low ≈ 51.45 × 1.105 ≈ 56.85 V
If the inverter allows a maximum DC voltage of 500V:
Max modules in series = 500 V ÷ 56.85 V ≈ 8.79 → 8 modules per string (safe)
So in a conservative design you can put up to 8 panels in series without crossing 500V, even in cold conditions. This is the core of PV array voltage calculation on the DC side.
Step 2 – Check the solar array MPPT range
Next, you must ensure the working voltage of the string (Vmp_array) sits inside the solar array MPPT range of the inverter.
For the 600W panel:
-
Vmp = 43.32 V
For the hybrid inverter:
-
MPPT range: 130–180 V
Formula
Vmp_array = Vmp_module × modules_in_series
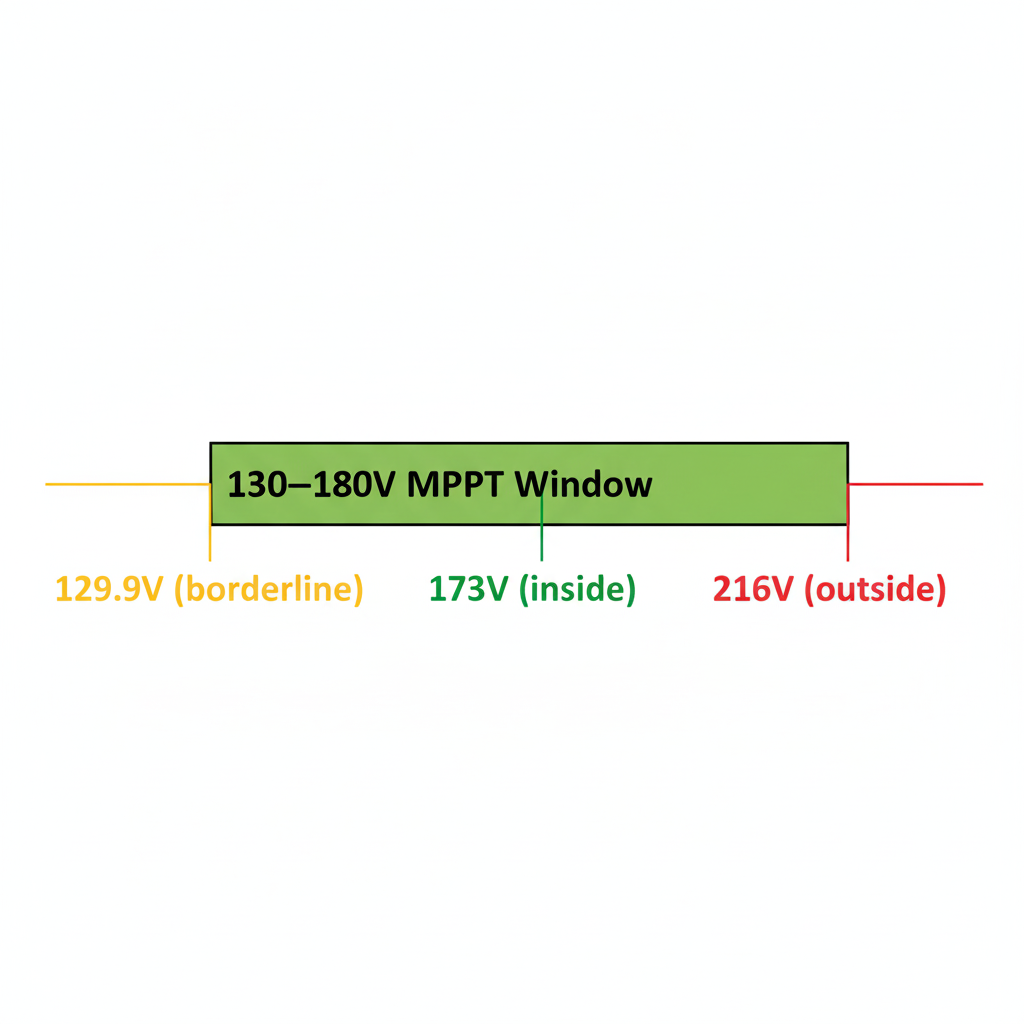
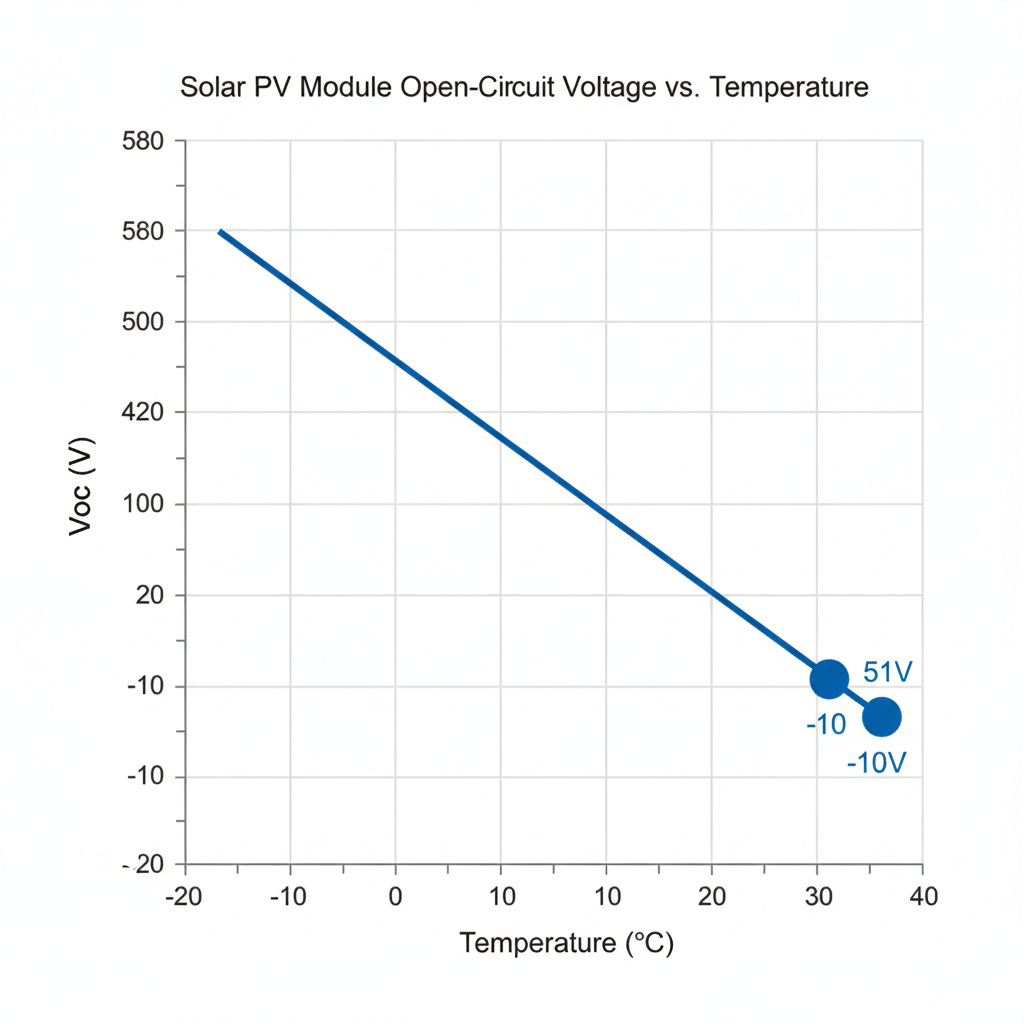
Check some options:
-
3 modules: Vmp_array = 43.32 × 3 ≈ 129.96 V → almost perfect
-
4 modules: Vmp_array = 43.32 × 4 ≈ 173.28 V → inside 130–180 V
-
5 modules: Vmp_array = 43.32 × 5 ≈ 216.60 V → above 180 V → not acceptable
For this solar inverter for PV array, each string should use 3–4 panels in series to stay inside the MPPT window.
Bifacial, double glass modules often show slightly more stable operating temperatures, which helps keep PV array open circuit voltage and Vmp closer to design values and reduces solar array hotspot problem in harsh conditions.
Step 3 – How many panels in a solar array for ~20kW?
Now estimate how many modules you need for your solar array system cost and power target.
Formula
Number of modules = Target array power ÷ Panel power
For a 20kW target:
-
20,000 W ÷ 600 W ≈ 33.3 → typically choose 32 or 36 modules
If we choose 32 modules and 4 modules per string:
Number of strings = 32 ÷ 4 = 8 strings
So the PV array configuration is:
-
4 modules in series
-
8 strings in parallel
-
Approx. 19.2 kW 600W solar panel array
This same logic works for a residential solar array, a small solar farm array, or a solar array kit with a different target size.
Step 4 – Basic PV array layout design
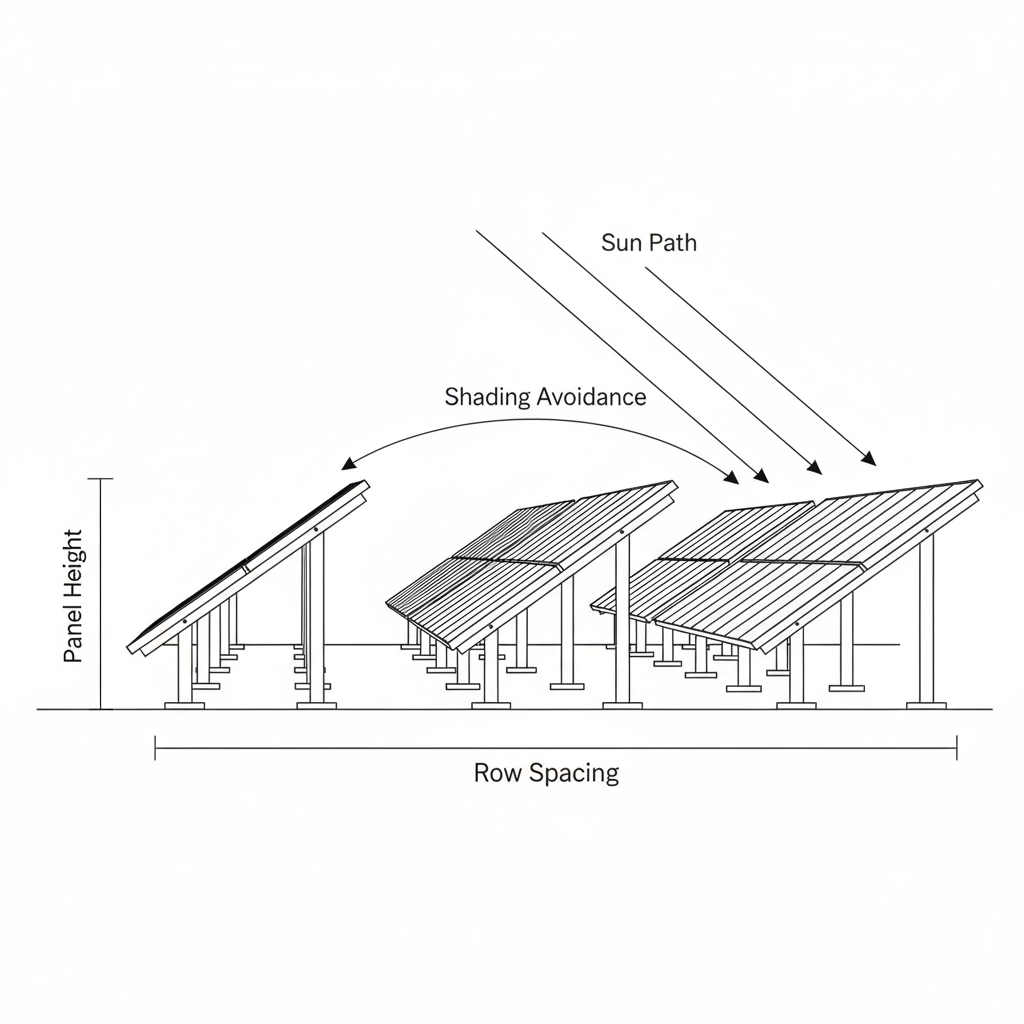
Panel size: 2279 × 1134 mm
If you put 8 modules in a row (portrait), the row length is roughly:
Row length ≈ 2.279 m × 8 ≈ 18.2 m
Row spacing depends on your PV array tilt angle and desired shading margin. A common rule of thumb used in many PV array spacing calculators:
Row spacing ≈ Module length × tan(critical sun angle)
In Jamaica, high sun angles help reduce shading, but storms demand strong mounting and good solar array stability. Whether you use a ground mounted solar array or a rooftop solar array system, design for wind, access, and maintenance, not only for kWh.
Step 5 – Battery and inverter compatibility
When you build a PV array with lithium battery, you must check voltage and current compatibility to avoid an incompatible inverter battery system.
For the battery:
-
Nominal voltage: 192 V
-
Max charge/discharge current: 120 A
-
Communication: CAN & RS485
For the inverter:
-
Battery DC rating: 240 V
-
AC charge current: 30 A
Two checks:
-
Voltage check
-
Confirm if the hybrid inverter can be configured to work with a 192V battery system (range setting).
-
This is crucial for any 192V battery solar system.
-
-
Current check
-
Inverter charge current (30 A) is well below battery max (120 A) → safe.
-
This is the basic logic behind any battery compatible PV array design, whether you aim for a small home solar array package or a mid-sized commercial solar array solution.
Step 6 – MPPT charge controller and PV array match
For the 48V MPPT charge controller PV array (LVC120A):
-
MPPT range: 65–150 V
-
Max PV input: 5200 W
-
Rated current: 120 A
Using the 600W panel:
-
2 in series:
-
Vmp_array ≈ 43.32 × 2 = 86.6 V → inside 65–150 V
-
Power per string: 600 × 2 = 1200 W
-
-
3 in series:
-
Vmp_array ≈ 129.96 V → inside range
-
Power per string: 1800 W
-
-
4 in series:
-
Vmp_array ≈ 173.28 V → above 150 V → not acceptable
-
So, for this high current MPPT solar array:
-
Use 2 or 3 panels in series for each string
-
Keep total PV power ≤ 5200 W per controller
-
Ensure combined string current does not exceed 120 A
This answers, in a practical way, how to size a PV array for MPPT and how to size a PV array with MPPT controller.
Making the System Island-Proof: Mobile Cabinets & Bifacial Modules
Mobile vs wall-mounted: flood-safe solar system design
In flood-prone areas, some users naturally ask for wall-mounted inverters and batteries “as high as possible”. From a safety perspective, that is not always ideal: heavy equipment on walls can become a risk in storms.
Sunchees takes a different approach:
-
Inverters, lithium batteries and controls are built into a movable solar power system cabinet with wheels.
-
The whole backend acts as a portable solar array system or off-grid mobile solar array back-end.
-
For flood-risk sites, the cabinet can be placed on a raised, solid platform instead of being hung on a wall.
This gives you:
-
Easier maintenance and solar array troubleshooting
-
The option to roll the system to a safer location if needed
-
A practical disaster relief solar array or backup power unit for solar array for remote areas
The panels themselves stay as a fixed solar PV array, but the “heart” of the system is movable, which suits island use very well.
Bifacial double glass solar PV array: more yield, fewer hot spots
Sunchees can upgrade the 600W panel to a double glass solar PV array (bifacial) at no extra cost:
-
Around 1.5%+ extra efficiency in many real sites
-
Extra energy from reflected light, especially on bright roofs or concrete
-
Reduced risk of solar array overheating and hot spots thanks to shingled interconnection and better thermal distribution
For a constrained rooftop solar panel array in Jamaica, or a tight solar photovoltaic array in a yard, this helps you get more kWh from the same area, and it directly addresses how to prevent hot spots in solar arrays.
Why Use One Vendor for Your Solar PV Array in Jamaica?
When you combine a solar battery array, a 20kW solar inverter array, a 120A MPPT PV system and a 600W 182mm solar panel array from different brands, you often spend more time on:
-
Protocol issues between inverter and BMS
-
MPPT tracking unstable with mixed PV strings
-
Unclear responsibility when something fails
Sunchees is positioned as a solar array manufacturer China and solar system supplier China that develops:
-
Inverter
-
Lithium battery
-
Control systems
in-house, so the PV array to battery wiring, communication and protections are designed to be compatible from day one.
Snapshot of Sunchees as a supplier
|
Category |
Details |
|
Brand |
Sunchees |
|
Founded |
2008 |
|
Location |
Foshan, Guangdong, China |
|
Factory scale |
Approx. 1000 km² |
|
Core tech |
In-house inverter + lithium battery, 100% system-level compatibility |
|
Customisation |
Solar array OEM; can use specified module brands; custom system & solar air-conditioning solutions |
|
System life |
Up to 25 years |
|
Installation |
Full remote guidance; ≥50kW systems get free on-site engineer |
|
Samples |
1–10 sets: 5–7 working days |
|
Bulk orders |
20–100 sets: 10–20 working days |
|
Delivery |
If shipment is late, Sunchees pays 5% of contract value as penalty |
|
Tracking |
Dedicated staff reports production progress |
|
Markets |
200+ countries and regions; strong presence in Caribbean & Latin America |
Warranty & packaging (for a complete solar array kit)
-
Modules: 10-year warranty, free replacement for quality issues
-
Lithium batteries: 3-year warranty, free replacement for leakage / deformation
-
Inverter / controller / combiner: 2-year warranty, free PCB replacement
-
Packaging:
-
Panels: carton + pallet
-
Inverter / combiner: wooden box
-
Controllers, batteries, cables: cartons
-
For buyers searching solar array wholesale, solar modules wholesale, or solar array bulk order, this kind of clarity around lead time, penalty and packaging is often as important as the datasheet itself.
FAQs: Solar PV Array in Jamaica
Q1. How to design a solar PV array in Jamaica for an off-grid home?
For a solar array for off grid homes:
-
Estimate daily and peak loads.
-
Decide target PV size (kW) and battery size (kWh).
-
Choose modules (e.g. 600W) and use PV array string sizing to define how many in series.
-
Check that Vmp_array sits inside the inverter MPPT voltage range.
-
Verify max DC voltage, Isc, and cable ratings.
-
Match a lithium battery for solar array and inverter that are designed to work together.
-
For flood-prone sites, put the backend system in a raised, mobile cabinet rather than on the floor.
A well-documented solar array installation guide from the supplier helps reduce mistakes.
Q2. How many panels in a solar array for a 20kW system?
If you use 600W panels:
20,000 W ÷ 600 W ≈ 33.3 → 32 or 36 panels in practice
For 32 panels with 4 in series:
-
4 modules in series → 8 strings in parallel
This is a simple but typical PV array string configuration. You can then refine it using a PV array calculator based on your exact inverter and controller.
Q3. Can I mix different panels in one PV array?
You can, but it is usually not recommended. Mixing panels with different power, voltage or current in the same solar array tends to:
-
Increase PV array mismatch loss
-
Make PV array shading analysis harder
-
Raise the chance of solar array hotspot problem
If you must mix, keep different panel types on separate MPPT inputs or even separate solar array kit segments.
Q4. Where should I place inverter and battery in a flood-prone area?
For a solar PV array for flood-prone areas:
-
Keep the solar panel array on a roof or elevated structure with proper mounting.
-
Place the inverter and battery in a movable solar power system cabinet on a raised, strong platform.
-
Avoid hanging heavy cabinets on walls that may see high wind loads.
-
Follow PV array safety requirements and local electrical codes for clearances and grounding.
A mobile cabinet can also act as a small disaster relief solar array backend if you need to power a different building after a storm.
If you are planning a solar PV array in jamaica and want to base your design on numbers instead of guesswork, the steps and examples above give you a repeatable method. Once the math and configuration are clear, choosing a supplier then comes down to:
-
technical compatibility,
-
delivery reliability, and how much help you get before and after the sale.
That is where a single-vendor, system-level approach like Sunchees can simplify both engineering and project risk.
For the full country-wide analysis, installation tips, inverter comparisons, and financing options, visit the Sunchees Jamaica Solar Hub




 Home
Home Sunchees Jamaica Solar Hub
Sunchees Jamaica Solar Hub  You May Also Like
You May Also Like






 Tel
Tel
 Email
Email
 Address
Address















